Jun 13, 2025
Eliquis vs. Warfarin: Cost, Effectiveness, and Alternatives for Blood Clot Treatment

THIS WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE. The content included on this website is for informational and educational purposes only. Always consult with your healthcare provider regarding any medical condition and before starting any healthcare or medication regimen.
Eliquis (apixaban) is a commonly prescribed blood thinner used to prevent and treat serious blood clots. While it’s known for its effectiveness and ease of use, Eliquis is also one of the more expensive anticoagulants on the market. Many patients are left wondering: is it worth the cost? And are there more affordable alternatives?
In this article, we’ll compare Eliquis with Warfarin, a long-established alternative. We’ll explore how each works, their side effects, monitoring requirements, and how to save money using a prescription discount card from CareCard.
Save up to 85% on prescriptions
Get free coupons and save up to 85% at the pharmacy.
Conditions Treated by Eliquis and Warfarin
Both medications are used to prevent or treat blood clots, particularly in the following conditions:
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): An irregular heartbeat that increases the risk of stroke and clots.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A clot that forms in deep veins, typically in the legs.
Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A potentially life-threatening condition in which a clot travels to the lungs.
Recurrent DVT/PE: Ongoing prevention of future clot events after an initial incident
Mechanical Heart Valves: Warfarin is often used in patients with artificial heart valves, where newer drugs are not recommended.
What Is Eliquis (Apixaban)?
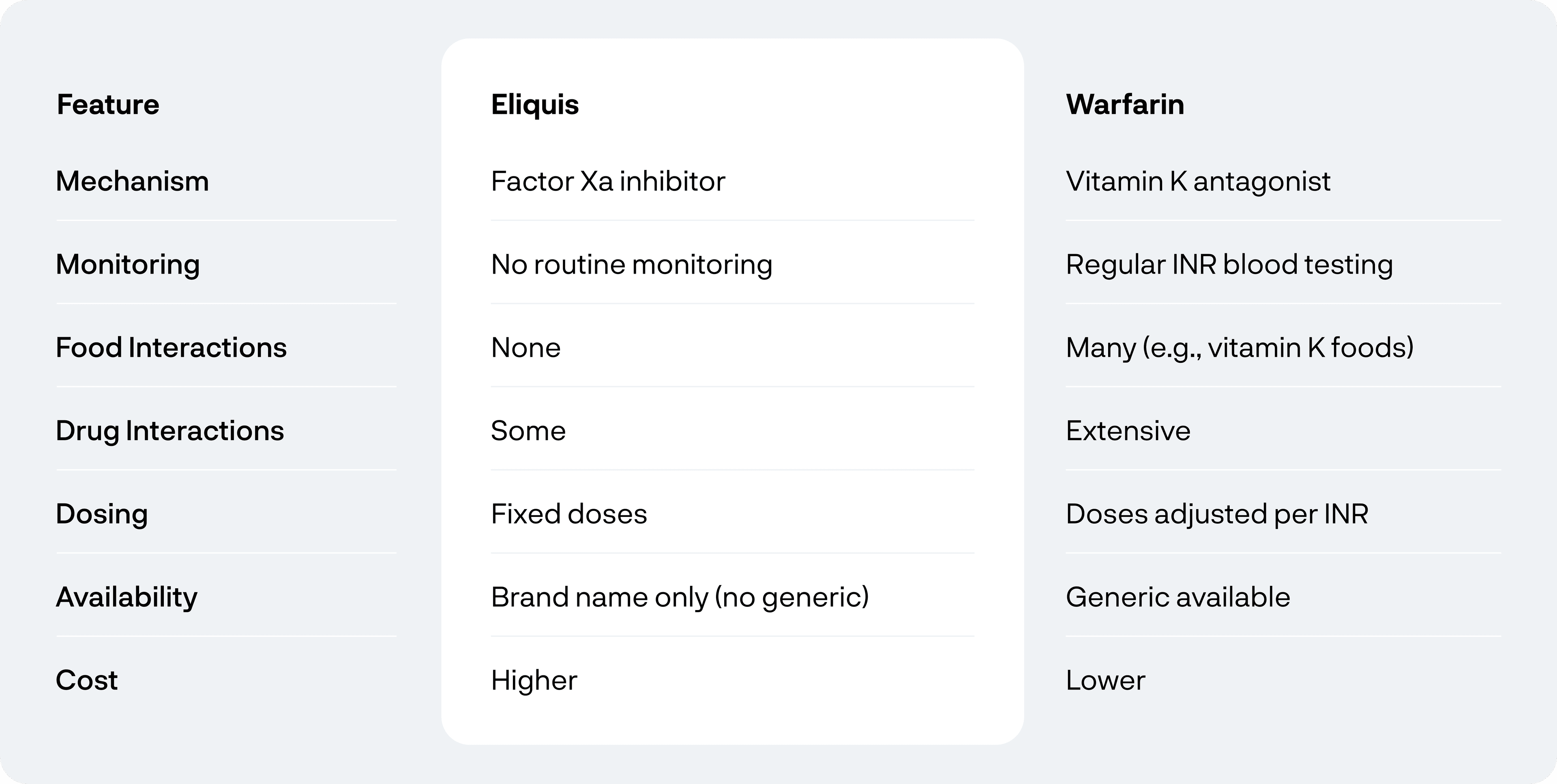
Eliquis is a prescription anticoagulant that works by inhibiting Factor Xa, an enzyme involved in the blood clotting process. By blocking this enzyme, Eliquis helps reduce the risk of clots forming in the veins or traveling to the lungs or brain.
Effectiveness of Eliquis
Eliquis has been proven to be highly effective for reducing the risk of stroke and blood clots in patients with atrial fibrillation and those with DVT or PE. Studies have shown that it is at least as effective as Warfarin, the older blood thinner, with a lower risk of bleeding complications.
How to Take Eliquis
For DVT/PE treatment: 10 mg twice daily for 7 days, followed by 5 mg twice daily
For AFib: 5 mg twice daily (lower dose for certain patients)
Eliquis does not require routine blood monitoring, which is a major convenience for many users.
Common Side Effects
Minor bleeding (bruising, nosebleeds)
Anemia
Nausea
Serious Side Effects
Severe internal bleeding (e.g., gastrointestinal or brain hemorrhage)
Allergic reactions (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing)
Drug Interactions
Eliquis may interact with:
Antiplatelet drugs (e.g., aspirin, clopidogrel)
Certain antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole)
HIV medications (e.g., ritonavir)
Always let your doctor know about any other medications or supplements you’re taking.
What is Warfarin?
Warfarin is an older anticoagulant that prevents blood clots by interfering with vitamin K, which is needed for clotting proteins to form. It’s effective but requires more intensive monitoring.
Effectiveness of Warfarin
Warfarin is highly effective for preventing strokes and managing blood clots, especially for those with mechanical heart valves. However, Warfarin requires regular blood tests (INR tests) to monitor clotting levels and adjust the dosage accordingly, which can be cumbersome for patients.
How to Take Warfarin
Taken once daily by mouth
Dosage varies and must be adjusted based on blood test results (INR)
Common Side Effects
Bleeding
Nausea
Skin rash
Serious Side Effects
Major bleeding ((e.g., gastrointestinal bleeding, brain hemorrhage)
Purple toe syndrome
(e.g., gastrointestinal bleeding, brain hemorrhage)
Drug and Food Interactions
Warfarin interacts with:
Many antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs
Leafy greens (due to vitamin K)
Herbal supplements (e.g., St. John’s Wort, ginseng)
Patients on Warfarin must be cautious about diet and other medications due to these interactions.
